Solo ALOHA Software Setup
Note
The Interbotix ALOHA Solo control software is supported for ROS 2 Humble running on native Linux Ubuntu 22.04.
Note
If using a laptop supplied by Trossen Robotics, all required software will be pre-installed. In this case, you can skip to the Post-Install Hardware Setup section of this guide.
This guide will walk through the process of setting up the Interbotix ALOHA Solo control software.
ROS 2 Installation
ROS 2 can be installed in one of two ways:
- (Preferred) Using the Interbotix X-Series Arm installation script. See the next section for details.
- Following the official ROS 2 Humble Ubuntu Debian install guide.
Interbotix X-Series Arm Control Software Installation
Follow the ROS 2 Standard Software Setup > AMD64 Architecture guide.
In short, run the following commands on a machine running Linux Ubuntu 22.04:
$ sudo apt install curl
$ curl 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Interbotix/interbotix_ros_manipulators/main/interbotix_ros_xsarms/install/amd64/xsarm_amd64_install.sh' > xsarm_amd64_install.sh
$ chmod +x xsarm_amd64_install.sh
$ ./xsarm_amd64_install.sh -d humble -n
The installation script does the following:
Installs ROS 2 Humble (if not already installed).
Creates the following directory structure:
~/interbotix_ws └── src ├── interbotix_ros_core ├── interbotix_ros_manipulators └── interbotix_ros_toolboxesInstalls dependencies.
Builds the control software and other related tools.
Configures the ROS 2 environment.
Tip
After running the install script, remove all added lines beneath the # Interbotix Configurations header in the ~/.bashrc file.
Doing so will make environment configuration easier later on.
ALOHA Software Installation
Clone the Interbotix fork of ALOHA into the workspace’s source directory:
$ cd ~/interbotix_ws/src $ git clone https://github.com/Interbotix/aloha.git -b 2.0
Run rosdep to install any dependencies:
$ cd ~/interbotix_ws $ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Set the
InterbotixManipulatorXS’siterative_update_fkdefault value toFalseat~/interbotix_ws/src/interbotix_ros_toolboxes/interbotix_xs_toolbox/interbotix_xs_modules/interbotix_xs_modules/xs_robot/arm.py(link).Build the workspace:
$ cd ~/interbotix_ws $ colcon build
Note
If planning to change the control or data collection software later on, you may want to do a symbolically-linked install.
If that is the case, remove the build and install directories, and re-run colcon build with the --symlink-install flag.
$ cd ~/interbotix_ws $ rm -rf build install $ colcon build --symlink-install
Post-Install Hardware Setup
The arm and cameras need to be bound to a unique device. The following sections will provide steps on setting up unique symbolic links for each device.
Arm Symlink Setup
We will configure udev rules to bind the arms to specific device names. Depending on the orientation of the pair you plan to use, configure the device names accordingly as either left or right:
ttyDXL_leader_leftfor the left oriented leader armttyDXL_follower_leftfor the follower armttyDXL_leader_rightfor the right oriented leader armttyDXL_follower_rightfor the follower arm
To set these up, do the following:
Plug in only the leader robot to the computer.
Determine its device name by checking the
/devdirectory before and after plugging the device in. This is likely something like/dev/ttyUSB0.Print out the device serial number by running the following command:
$ udevadm info --name=/dev/ttyUSB0 --attribute-walk | grep ATTRS{serial} | head -n 1 | cut -d '"' -f2 FT88YWBJ
The output of the command will look like
FT88YWBJand be the serial number of the arm’s U2D2 serial converter.Add the following line to the computer’s Interbotix udev rules file located at
/etc/udev/rules.d/99-fixed-interbotix-udev.rules. You only need to configure a leader and a follower. The orientation (left or right) depends on your choice. If you use a right leader, ensure you pair it with a right follower, and similarly for the left orientation. Update the serial number and symlink name accordingly for your chosen configuration:SUBSYSTEM=="tty", ATTRS{serial}=="<SERIAL NUMBER>", ENV{ID_MM_DEVICE_IGNORE}="1", ATTR{device/latency_timer}="1", SYMLINK+="ttyDXL_leader_left" # ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ The result from the previous step
Repeat for the other arm.
To update and refresh the rules, run the following command:
$ sudo udevadm control --reload && sudo udevadm trigger
Plug both arms back into the computer and verify that you can see all devices. Depending on whether you configured the arms for a left or right orientation, you will see the corresponding device names:
$ ls /dev | grep ttyDXL_For a left orientation, you should see:
ttyDXL_leader_left ttyDXL_follower_leftFor a right orientation, you should see:
ttyDXL_leader_right ttyDXL_follower_right
Camera Setup
Open realsense-viewer
$ realsense-viewer
Note
If realsense-viewer is not already installed on your machine, follow these steps on the librealsense GitHub repository to install
librealsense2-utils.Plug in a single camera and check the sidebar for its entry. If it does not show up in the side bar, click Add Source and find the Intel RealSense D405 in the drop down.
Click on Info for the camera, find the Serial Number, and copy it.
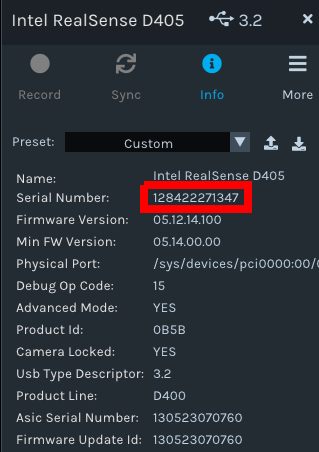
Put the camera serial number in the appropriate config entry at
~/interbotix_ws/src/aloha/config/robot/aloha_solo.yaml.Repeat for the other camera. If the workspace has not been symbolically-linked, a rebuild may be necessary.
Post-Install Software Tips
Disable wandb
It may be helpful to disable wandb while getting started. To do so, run the command below. Note that this line is added by default to the laptops distributed by Trossen Robotics.
$ echo "WANDB_MODE=disabled" >> ~/.bashrc
Alias Setup
It may be helpful to create bash aliases to make environment configuration easier.
Create a ~/.bash_aliases file:
$ touch ~/.bash_aliases
To create an alias that can be used to set up the ROS 2 environment, add the following line to the ~/.bash_aliases file:
alias setup_aloha="source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash && source ~/interbotix_ws/install/setup.bash"
Assuming that dependencies of ACT were installed using a venv, to create an alias that can be used to set up the ROS 2 and ACT environments, add the following line to the ~/.bash_aliases file:
alias setup_act="setup_aloha && source /<path_to_aloha_venv>/bin/activate"